 cloning, the process of generating a genetically identical copy of a cell or an organism. Cloning happens often in nature—for example, when a cell replicates itself asexually without any genetic alteration or recombination.
cloning, the process of generating a genetically identical copy of a cell or an organism. Cloning happens often in nature—for example, when a cell replicates itself asexually without any genetic alteration or recombination.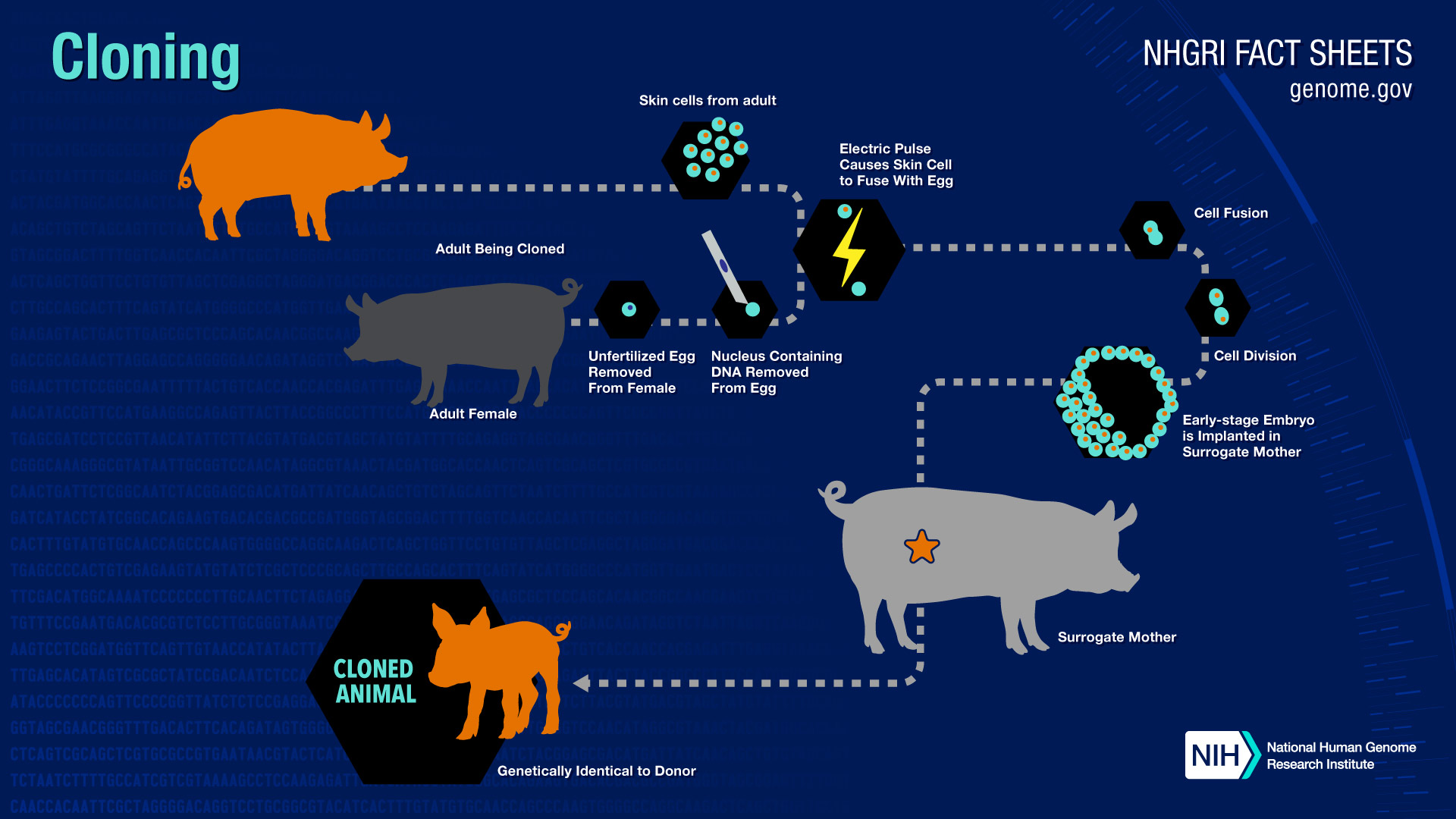 The term cloning describes a number of different processes that can be used to produce genetically identical copies of a biological entity. The copied material, which has the same genetic makeup as the original, is referred to as a clone.
The term cloning describes a number of different processes that can be used to produce genetically identical copies of a biological entity. The copied material, which has the same genetic makeup as the original, is referred to as a clone. Cloning is the process of producing individual organisms with identical genomes, either by natural or artificial means. In nature, some organisms produce clones through asexual reproduction; this reproduction of an organism by itself without a mate is known as parthenogenesis.
Cloning is the process of producing individual organisms with identical genomes, either by natural or artificial means. In nature, some organisms produce clones through asexual reproduction; this reproduction of an organism by itself without a mate is known as parthenogenesis. Cloning describes the processes used to create an exact genetic replica of another cell, tissue or organism. The copied material, which has the same genetic makeup as the original, is referred to as a clone.
Cloning describes the processes used to create an exact genetic replica of another cell, tissue or organism. The copied material, which has the same genetic makeup as the original, is referred to as a clone.